The use of Machine Learning (ML) algorithms in the field of big data analysis has been a thing of paramount importance in the current information age. In the context of scientific computing, ML models implementing these algorithms serve as a faster means to get to the results than pure iterations. In this article, we will look at one of the supervised ML models called — Random Forest model. Before that, we need to understand two basic techniques that serve as its backbone, namely — Decision trees and Ensemble learning.
What are Decision Trees?
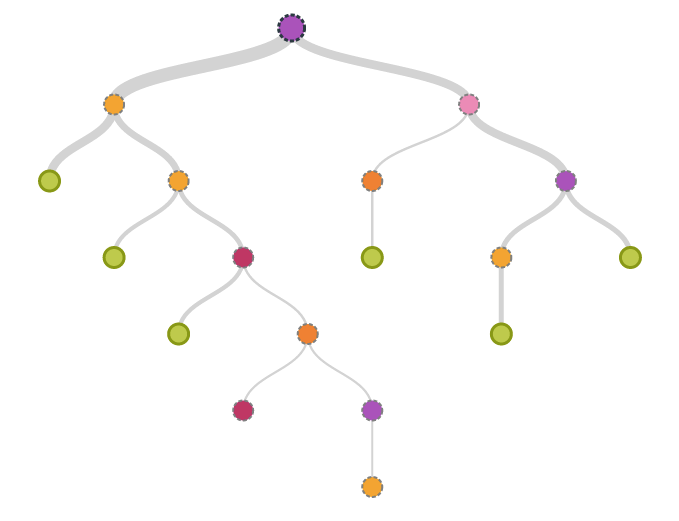
To understand decision trees better we take an example of a popular application called Akinator. If you have never used it, in short, it’s a game that accurately predicts any object or character that you think of. The objective is to ask you a set of questions and reach a conclusion — found in the Terminal node. The game implements decision trees, whose structure begins with a root node that eventually splits into branches based on conditions and end up on other nodes. The terminal node is often called the leaf node that marks the conclusion of the tree. Splitting at a node is done based on different classes present in the original dataset used to train the tree. A popular metric is called the Gini Index which is the sum of squared probabilities of elements in a class used to make the split. If the Gini Index of one class is greater than the other, then that class qualifies to be a better split.
An optimal number of splits known as the depth of the tree is required to make the most accurate prediction. If a tree has large depth then data may be ‘over-fitted’ which means the tree will work well with the training dataset but not fine with the testing dataset. The opposite condition is called ‘under-fitting’ that involves too low depth of the tree to make predictions.
What is Ensemble Learning?
Though decision trees seem simple enough to be implemented by using any standard packages, the accuracy of a single decision tree may not be as per the desired value because of its high dependency on the training dataset. Often a metric called mean absolute error is used to validate an ML model. A better way to train the model is by using random samples that are trained by individual models. The final predictions of all these models can be averaged out to minimize the mean absolute error value and hence improve the accuracy. This technique is called ensemble learning and when implemented using decision trees, we get the random forest model.
An ensemble learning method can be applied for parallel predictive models as well as sequential models. These techniques are themselves called bagging, boosting and stacking.
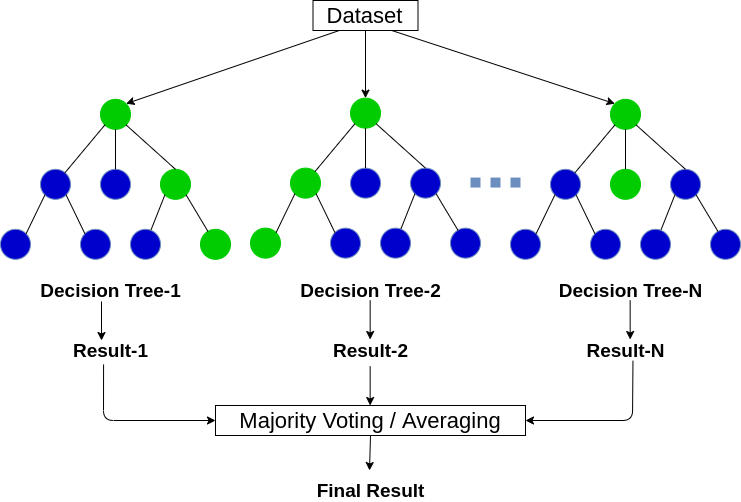
Random Forest Model
A forest is a collection of trees, so a random forest is a collection of random trees. The randomness can be specified using different algorithms and random samples from the training dataset may be used to train random trees. The overall model averages out the predictions of each of these random trees to make the final prediction.
It is a model to solve regression classification problems in a supervised manner. The accuracy of this model can be validated by the same mean absolute error.
How to implement Random Forest Model?
There are many standard libraries in Python and R that can be used to import ML models in your code. We can use python’s sklearn package as an example.
The steps involved in the implementation are:
- Specifying prediction target/dependent variable (y)
- Creating features/independent variables set (X)
- Cleaning data and fixing missing values
- Importing RandomForestRegressor from sklearn.ensemble package to create an object of that class
- Importing mean_absolute_error from sklearn.metrics to create an object which will hold the validation
- Fitting the model using train set of X and Y
- Predicting values of y for test set using the fitted model
- Validating the model with the predicted values.
Conclusion:
The accuracy of the decision tree model can be increased by the use of ensemble learning and hence converting it to a random forest model. To further deal with underfitting and overfitting we may use the max_leaf_nodes argument of the regressor function that may be assigned the optimal no. of nodes for doing the prediction. A for loop iteration with mean absolute error values for each iteration can be used to determine the optimal number of nodes having minimum error value. Thus, the Random Forest model can be used as a supervised model in different aspects of scientific computing.
Devi Dutta Biswajeet contributed to this article. I thank him for taking the time off his busy schedule to write this informative article. The information presented in this article is the sole responsibility of the author.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.